Introduction
Environmental stewardship is a concept that transcends cultural and religious boundaries. Many religions across the world emphasize the importance of caring for the Earth, advocating for sustainable living and respect for nature. This article explores how various religious teachings influence environmental stewardship, comparing perspectives from Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Indigenous spiritualities.
Christianity
Christianity’s approach to environmental stewardship is rooted in the belief that God created the Earth and entrusted humans with its care. The Bible emphasizes stewardship and the responsibility of humans to protect and preserve the natural world.
In Genesis 2:15, it is written, “The Lord God took the man and put him in the Garden of Eden to work it and take care of it.” This verse highlights the responsibility given to humans to tend and protect the Earth. Many Christian organizations have adopted this principle, promoting sustainable practices and environmental conservation.
Pope Francis, in his encyclical “Laudato Si’,” calls for urgent action to protect the environment. He states, “We must regain the conviction that we need one another, that we have a shared responsibility for others and the world” (Pope Francis, Laudato Si’). This document has been instrumental in galvanizing the Christian community towards environmental activism.
Islam
Islamic teachings also emphasize the importance of environmental stewardship. The Quran contains numerous references to nature and the environment, encouraging Muslims to protect and cherish the Earth.
The Quran states, “And do not commit abuse on the earth, spreading corruption” (Quran 2:60). This directive encourages Muslims to avoid causing harm to the environment. Additionally, the concept of “Khalifa” (stewardship) in Islam underscores the duty of humans to act as caretakers of the Earth.
Imam Zaid Shakir, a prominent Islamic scholar, explains, “Environmental stewardship is an integral part of our faith. We are entrusted by Allah to take care of His creation, and this is a responsibility we must take seriously” (Shakir, 2010). Many Islamic organizations have launched initiatives to promote sustainable practices and raise awareness about environmental issues.
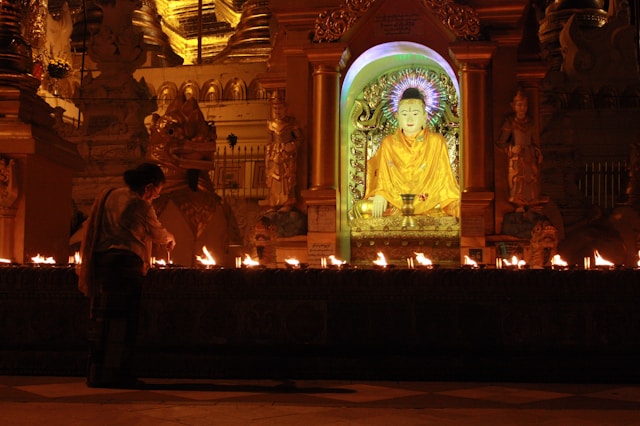
Buddhism
Buddhism’s perspective on environmental stewardship is deeply rooted in the principles of interconnectedness and compassion for all living beings. The concept of “Ahimsa” (non-violence) extends to all aspects of life, including the treatment of the environment.
Thich Nhat Hanh, a renowned Buddhist monk, emphasizes, “When we recognize the virtues, the talent, the beauty of Mother Earth, something is born in us, some kind of connection; love is born” (Hanh, 2012). This connection fosters a sense of responsibility towards protecting the environment.
The Buddhist practice of mindful living encourages individuals to live sustainably and harmoniously with nature. Buddhist communities often engage in environmental conservation projects, such as reforestation and promoting plant-based diets to reduce ecological footprints.
Hinduism
Hinduism’s environmental ethics are derived from ancient scriptures that highlight the sanctity of nature. The concept of “Dharma” (duty) includes the responsibility to protect the environment.
The Atharva Veda, an ancient Hindu scripture, proclaims, “The Earth is our mother, and we are her children” (Atharva Veda 12.1.12). This verse underscores the intrinsic relationship between humans and the Earth, promoting a sense of reverence and duty towards environmental preservation.
Ravi Shankar, a spiritual leader, notes, “In Hinduism, the Earth is revered as a goddess. This reverence translates into a duty to protect and sustain the environment” (Shankar, 2015). Hindu festivals and rituals often incorporate environmental themes, encouraging eco-friendly practices.
Indigenous Spiritualities
Indigenous spiritualities are inherently connected to nature, viewing the Earth as a living entity with which they share a profound relationship. These spiritual traditions emphasize respect, reciprocity, and sustainability.
Winona Williams, a local activist from https://kingbilly.online/, explains, “For Indigenous peoples, the land is sacred. Our traditions teach us to live in harmony with nature and to take only what we need”. This worldview promotes sustainable living and the protection of natural resources.
Indigenous communities worldwide engage in practices such as sustainable agriculture, conservation of biodiversity, and protection of water sources. These practices are deeply rooted in their spiritual beliefs and cultural heritage.
Comparative Analysis
While the specifics of environmental stewardship vary across religions, there is a common thread of respect and responsibility towards the Earth. Each tradition offers unique insights and practices that contribute to environmental conservation.
Christianity and Islam emphasize stewardship and the duty to care for creation, with teachings that promote sustainable practices. Buddhism and Hinduism highlight interconnectedness and reverence for nature, encouraging mindful living and ecological harmony. Indigenous spiritualities focus on living in balance with nature, guided by traditions of respect and reciprocity.
The influence of religion on environmental stewardship is profound and multifaceted. By examining the teachings and practices of various religious traditions, we can gain a deeper understanding of how spiritual beliefs shape our interactions with the environment. These perspectives can inspire collective action towards a more sustainable and harmonious world.
As we face global environmental challenges, the wisdom embedded in these religious traditions offers valuable guidance. By integrating these teachings into our lives and communities, we can foster a culture of stewardship that honors and protects the Earth for future generations

 by
by 

